Introduction to Forensic Audits in Singapore
Achieving this, however, is easier said than done. Documenting your finances in a company that transacts on so many different levels presents various challenges and risks, such as susceptibility to accounting errors, financial mismanagement, regulatory breaches, or in some cases, fraud. These challenges, if left unaddressed, can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal consequences. On top of that, Singapore’s reputation as a leading financial hub with unwavering integrity necessitates maintaining a stringent regulatory framework that requires businesses to uphold the highest standards of accountability.
This is why financial auditing is necessary, whether it is done internally or by a neutral third party. They ensure that the books are in order and no foul play is afoot. Amongst the various kinds of auditing services available, forensic audits have emerged as a powerful tool to tackle these challenges. Unlike standard audits, forensic audits combine accounting expertise with legal acumen to investigate financial records thoroughly. These audits aim to uncover discrepancies, detect fraudulent activities, and compile evidence that can be used in legal or regulatory proceedings.
The role of forensic accounting cannot be overstated. As a financial hub with a diverse range of industries, Singapore is a hotbed for complex financial transactions. This creates an environment where forensic audits are essential not only for identifying transgressions, but also for preventing it.In this article, we will take an in-depth look at forensic audits in Singapore, delving into their definition, objectives, methodologies, and significance whilst shedding light on their practical applications and the value they bring to organisations.
Why Financial Transparency Matters
Financial transparency isn’t just a legal requirement; it builds trust. Clear and accurate reporting through professional auditing services helps investors, stakeholders, and partners make informed decisions while strengthening your company’s credibility in Singapore’s competitive business landscape.
Risks Such as Fraud, Mismanagement, and Regulatory Breaches
Businesses face risks like fraud, mismanagement, and regulatory breaches that can lead to financial losses and reputational damage. Employing forensic accounting techniques helps identify and mitigate these risks early, protecting your company and maintaining stakeholder confidence.
Importance of Stringent Financial Governance in Singapore
Strong financial governance ensures your company meets Singapore’s strict regulatory standards and the audit requirement in Singapore. Effective policies, robust internal controls, and consistent monitoring help safeguard assets, reduce risks, and demonstrate accountability to investors and regulators alike.
How Forensic Audits Differ from Regular Audits
Forensic audits go beyond standard financial checks. While regular audits focus on accuracy, forensic audits leverage forensic accounting to investigate fraud, misconduct, and financial irregularities, providing detailed evidence that protects your business from legal and financial consequences.
What Is a Forensic Audit?

Definition of a Forensic Audit
Carried out by highly trained forensic accountants, these audits involve a meticulous examination and scrutinisation of financial data. The main goal is not only to identify irregularities, but also to understand the methods used to perpetrate fraud and quantify the resulting financial impact.
Types of Forensic Audits
The two main types of forensic audits are:
Fraud Audits:
These audits are conducted to detect, investigate, and gather evidence related to fraud, financial misconduct, or any illegal activity. They focus on identifying fraudulent transactions, misappropriation of assets, and manipulation of financial records. The goal is to uncover intentional wrongdoings and gather evidence that can be used in legal proceedings.
Financial Audits:
This type of audit is conducted to review financial statements and records to ensure they are accurate and compliant with relevant laws and regulations. While not primarily focused on fraud detection, financial audits can uncover irregularities that may point to fraudulent activity, especially when inconsistencies or discrepancies are found in the financial reports.
Both types of forensic audits involve detailed examination and analysis, but fraud audits are more specifically geared towards identifying and investigating wrongdoing.
Key Objectives of Forensic Audits
Forensic audits are a vital tool for businesses seeking to maintain financial integrity, uncover discrepancies, and mitigate risks in their financial operations. These audits delve deep into financial records with a focus on identifying fraud, reinforcing internal controls, and providing actionable evidence for legal purposes. By systematically addressing key vulnerabilities, forensic accounting not only safeguards an organisation’s assets but also fosters a culture of transparency and accountability.
Detecting Instances of Fraud
One of the foremost objectives of forensic audits is to detect fraudulent activities within an organisation. Fraud can manifest in various forms, such as embezzlement, falsification of financial statements, or unauthorised financial transactions. Forensic auditors use advanced investigative techniques to identify irregularities, such as analysing anomalies in transactional data, reconciling accounts, and tracing suspicious financial flows. By thoroughly scrutinising financial records, auditors uncover patterns of fraudulent behaviour and pinpoint the individuals or processes responsible. Early detection of such activities is critical in limiting financial losses and preventing further damage to the organisation’s reputation.
Preventing Fraud
Beyond detection, forensic auditing plays a proactive role in fraud prevention. As the age-old saying goes, prevention is better than cure. By identifying weak points in an organisation’s internal controls, auditors help design and implement measures to minimise the risk of future fraud. This involves evaluating the effectiveness of current procedures, recommending system upgrades, and establishing comprehensive checks and balances. Adopting such preventive measures not only deters potential fraudulent activities but also enhances the organisation’s overall operational efficiency. Following the guidance and recommendations provided by forensic auditors ensures compliance with industry best practices and regulatory standards, further reducing vulnerabilities to fraud.
Involving Auditors in Fraud Prevention Initiatives
Forensic auditors also contribute to the development of broader fraud prevention strategies. Drawing from their expertise in financial systems and fraud schemes, they collaborate with organisations to create customised fraud prevention initiatives. These initiatives may include employee training programmes on recognising fraud indicators, establishing whistleblowing mechanisms, and fostering a corporate culture of ethical behaviour. By actively engaging auditors in the design and implementation of these strategies, businesses build a robust framework for early fraud detection and deterrence.
Conducting Investigations and Gathering Evidence
Forensic audits are instrumental in conducting thorough investigations when fraud is suspected or reported. Auditors meticulously review financial records, digital communications, and other relevant documentation to gather evidence. This evidence serves multiple purposes—it provides clarity on the nature and extent of the fraudulent activity, identifies those responsible, and quantifies the financial impact on the organisation. Moreover, forensic auditors ensure that all collected evidence adheres to legal standards, making it admissible in judicial proceedings. Their detailed reports and expert testimonies play a critical role in pursuing legal action against wrongdoers and recovering misappropriated funds.
In short, the objectives of forensic accounting and reporting extend beyond merely addressing financial discrepancies. They encompass a comprehensive approach to detecting and preventing fraud, strengthening internal controls, and equipping organisations with the tools to navigate complex financial challenges. This in turn empowers businesses to build resilience and maintain their stakeholders’ trust in an increasingly complex financial landscape.
Why Forensic Audits Matter for Organisations
Forensic audits are essential for organisations, delving into financial records to detect and resolve irregularities, support legal proceedings, and prevent future misconduct. The importance of forensic audits lies in their ability to address complex challenges whilst promoting transparency and accountability in financial operations. Here are some examples of their significance across key areas.
1. Fraud Detection and Prevention
As mentioned earlier, forensic auditing is a primary line of defence against fraudulent activities, such as embezzlement and financial statement manipulation. This proactive approach mitigates fraud, ensures financial integrity, and provides organisations with actionable strategies to safeguard assets and prevent recurrence.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with legal and regulatory frameworks is non-negotiable for businesses, especially in jurisdictions like Singapore, known for its rigorous financial standards. Forensic audits ensure organisations adhere to these laws by identifying violations, such as misreporting or non-compliance with anti-money laundering statutes. Upholding compliance not only prevents legal penalties but also reinforces the broader integrity of the financial system, instilling trust amongst stakeholders.
3. Complex Financial Transactions
Forensic auditors excel at analysing intricate money flows, including cross-border transactions, derivatives, and investment vehicles. Their scrutiny helps uncover anomalies, ensuring transparency and legality in financial dealings. This is particularly critical for identifying money laundering and other illicit financial activities that could undermine organisational and national financial security.
4. Dispute Resolution
In legal disputes, such as shareholder conflicts and commercial litigation, forensic auditing provides clarity and fairness. Forensic accountants assess financial details, trace contested funds, and present sound testimony in court. Their ability to simplify complex financial data ensures accurate resolution, empowering parties to make informed decisions based on verified information.
5. Due Diligence
Forensic audits play a pivotal role in due diligence during mergers and acquisitions. By evaluating a target company’s financial health, auditors uncover hidden liabilities or irregularities that could impact the deal. This ensures that stakeholders receive accurate information that could influence their decisions, minimising risks and improving the overall success of the transaction.
6. Corruption and Bribery Investigations
Forensic auditors are indispensable in identifying corruption and bribery. By tracing suspicious transactions and gathering evidence, auditors help organisations address unethical practices. These investigations not only expose wrongdoing but also strengthen anti-corruption frameworks, fostering a culture of ethical accountability.
7. Asset Tracing
In cases of fraud or embezzlement, forensic auditing facilitates the tracing of misappropriated assets. Whether funds have been hidden or moved offshore, forensic accountants utilise advanced techniques to locate and recover assets, restoring financial stability and compensating affected parties.
8. Cybercrime and Data Breaches
With the rise of cybercrime, forensic audits help quantify financial losses from data breaches and cyberattacks. By tracing the financial implications of these incidents, auditors identify perpetrators and recommend measures to strengthen cybersecurity. This dual focus on accountability and prevention safeguards organisations from future threats.
9. Financial Auditing
Forensic auditors ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial records. This is critical for upholding stakeholder confidence and maintaining transparency in an organisation’s accounting practices. Enhanced financial integrity supports strategic decision-making and helps businesses comply with legal obligations.
10. Reputation Management
Finally, forensic auditors protect and restore organisational reputations by addressing instances of financial misconduct. This in turn prevents long-term damage to an organisation’s public image, reinforcing credibility amongst investors, customers, and regulatory bodies.
In short, forensic auditing is integral to detecting, addressing, and preventing financial irregularities. They enable organisations to operate ethically, adhere to regulations, and maintain stakeholder trust.
The Forensic Audit Methodology
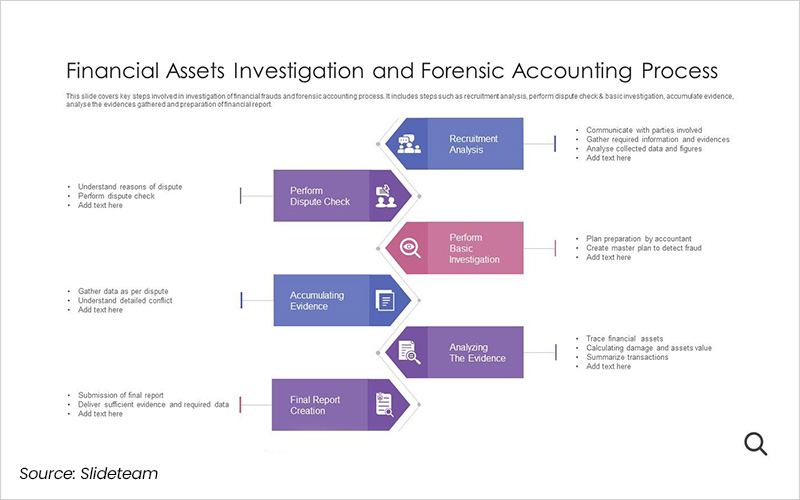
Forensic auditors follow a structured approach to uncover financial irregularities and compile evidence. The process can be broken down into four key phases:
Step 1: Audit Planning
The planning phase is critical to the success of a forensic audit. It involves:
- Clearly defining the audit’s objectives and scope.
- Identifying the issues or allegations to be investigated.
- Establishing a timeline for the audit.
Auditors collaborate with stakeholders to prioritise key investigative goals, such as identifying perpetrators, understanding fraudulent schemes, and quantifying financial losses.
Step 2: Collecting and Preserving Evidence
This phase involves gathering and preserving evidence to support the investigation. Auditors review financial records, contracts, and other relevant documents, employing techniques such as:
- Reconciling financial reports to identify discrepancies.
- Analysing data for unusual patterns or trends.
- Conducting interviews with employees and stakeholders.
Precautions are taken to ensure the integrity of evidence, including secure storage and detailed documentation of methodologies used.
Step 3: Reporting Audit Findings
The findings of the audit are consolidated into a detailed report, which serves multiple purposes:
- Summarising the investigation’s objectives, scope, and findings.
- Explaining how fraudulent activities were carried out.
- Quantifying financial damages and identifying perpetrators.
- Providing recommendations to prevent future incidents.
As part of comprehensive financial auditing, the report may also include legal guidance, assisting organisations in pursuing charges or initiating recovery actions.
Step 4: Supporting Court Proceedings
Forensic auditors often play a key role in legal proceedings. Their responsibilities include:
- Presenting findings in a clear and concise manner.
- Serving as expert witnesses to explain complex financial concepts.
- Collaborating with legal teams to strengthen the case.
3.2. Forensic Audits vs Internal Audits
Forensic audits differ significantly from internal audits in terms of purpose, methodology, and outcomes. While internal audits focus on ensuring compliance and operational efficiency, the former is investigative and often tied to legal or regulatory proceedings.
Key Differences in Purpose
While both audits aim to ensure financial accuracy and compliance, their purposes differ significantly. Internal audits focus on improving operational efficiency, monitoring internal controls, and supporting routine governance. Forensic audits, on the other hand, are investigative in nature, designed to detect fraud, misconduct, or financial irregularities and provide evidence for legal proceedings.
Differences in Methodology and Outcomes
Internal audits typically follow a structured, periodic review process, assessing policies, procedures, and compliance. Forensic audits use in-depth investigative techniques, such as detailed transaction tracing and data analysis, to uncover hidden fraud or mismanagement. The outcome of forensic audits is often a detailed report suitable for legal action, whereas internal audits primarily result in recommendations to strengthen internal controls and operational processes.
Frequently Asked Questions About Forensic Audits
Q: What types of issues can forensic audits investigate?
Forensic auditing addresses issues such as corporate fraud, embezzlement, bribery, whistleblower complaints, financial mismanagement, and cybercrime. By leveraging professional forensic accounting services, organisations can investigate these issues thoroughly, uncover irregularities, and implement measures to protect their financial integrity.
Q: How does Credo Assurance approach forensic audits?
Credo Assurance adopts a systematic approach, combining meticulous planning, thorough evidence collection, and expert reporting to support legal proceedings.
Q: How can organisations prevent fraud?
Fraud prevention begins with implementing strong internal controls and meticulous periodic reviews. Reputable audit firms in Singapore like Credo Assurance offer tailored strategies to identify vulnerabilities and implement safeguards.
Forensic audits are a cornerstone of financial transparency and accountability. In Singapore, where regulatory standards are stringent, and financial transactions are complex, these audits are indispensable for mitigating risks, ensuring compliance, and protecting reputations.
At Credo Assurance, we pride ourselves on delivering expert forensic auditing services that meet your organisation’s needs. With over 17 years in the industry, we are well-versed in a wide range of services, from fraud detection to asset recovery.
For more information or to get started, please contact us today.




